Brief instruction to CNKI Express 2.0
1. What are the entries of CNKI Express 2.0?
(1)Website 1: https://oversea.cnki.net/
Users can visit the home page of CNKI Express 2.0 through this website, which has the same style as that of https://www.cnki.net/.
(2)Website 2: https://oversea.cnki.net/kns/
Users can visit the home page of integrated databases through this website and achieve the same search results with the website 1. The page also provides personalized functions, such as Follow, Hot Recommendations, Popular Documents and Personal Study.
2. What products can be searched on this platform?
This platform covers products of journals, theses, proceedings, newspapers, yearbooks, patents, standards, achievements, books, ancient books, monographic serials, and featured journals.
3. How to select the product types for search according to needs?
Select products for cross-database search using the following two methods:
(1) Select products in the home page
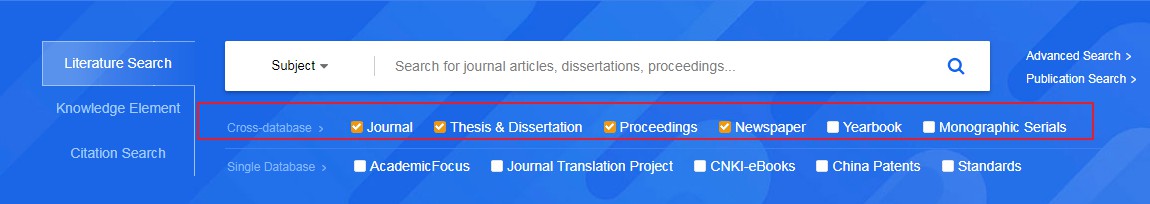
(2) Delete or add product types through clicking "Search Setting" on the top of the page

4. How to view documents according to product types after the search?
After the integrated database search, click the name of various product types, and these types of documents will be shown in the Search Result Area below.
For example, integrated database search results are as shown below:

Click "Academic Journal" to obtain journal documents.

5. What is the single database entry?
If you only want to search a certain type of documents, you can enter the single database through the entry:
(1) You can enter the home page of the single database by clicking the name of different products in the home page to conduct one-stop search.


(2) Click the name of products in the search result page of integrated database one-stop search, select search items and then click "Search" button after entering search terms in the search box.
General database search results:

Click the name of single database:

Click "Search" button to conduct single database search:

(3) Click "Advanced Search" in the home page or switch into "Advanced Search" from one-stop search, and switch database below the "Advanced Search" page to enter single database advanced search.



6. How are articles sorted in various groups?
The contents of most groups are sorted according to the number of documents. Some groups adopt special sorting standards. These groups will also provide authoritative recommended terms.
Sort by author: display after the sorting of authors' H index.
Sort by journal in the journal database: display after the sorting of journals' CI index.
7. How to use professional search?
Professional search is to conduct search with the help of SQL sentence. When using professional search, it is necessary to enter clear search fields and form search formulas using <field name><matching operator>< search value >. Take “KY='Knowledge Service' AND (AU % 'Chen'+'Wang' )” as an example, KY and AU can be replaced with your own search fields, = or % can be replaced with corresponding matching operators according to your needs, and KY and AU search fields are connected with AND, OR and NOT. The relationship of multiple values in the field can be expressed with +, - and *, or the grammar symbols for limiting location.

8. Why are there a lot of English articles in the search results? How to obtain the original texts of foreign language documents?
CNKI provides integrated search of foreign language documents and Chinese documents through the expansion of Chinese and English search words. The search results will contain foreign language documents data in case you don't click “Chinese”. At present, CNKI has conducted copyright cooperation with more than 650 publishing houses in more than 60 countries and regions. It includes more than 70,000 kinds of foreign language journals, covering 90% of SCI and over 80% of SCOPUS, and millions of books. You can obtain the full text of foreign language documents through clicking the full text link provided by the publishing house partnering with CNKI.
9. What personalized functions can users operate after signing up?
Users can enjoy the following services after free signing up:
(1) Save the integrated database search settings, such as the default cross-database search and search sorting.
(2) Use the relevant functions provided by Personal Study, such as documents collection, citation tracking, search subscription, documents recommendation, personal achievement management and various history records in the search results page.

(3) View Follow and personalized recommendations in the home page of the single database.


The demo video of CNKI Express 2.0
Search Method > basic search
Features of basic search
It conducts search through a search box, and adopts different search mechanism and matching modes according to the requirements of different search items, which represents the advantages of intelligent search, such as easy operation, and complete and precise search results.
Operation methods
Click "Search Scope" in the home page of the platform, select search items in the drop-down menu, enter search terms in the search box, and then click "Search" button or press "Enter" to perform the search. See Fig. 1.2.1.2.

Search items
The general database provides the following search items: subject, keyword, title, full text, author, the first author, corresponding author, author’s affiliation, fund, abstract, reference, CLC number and document source.
(1) Subject search
Subject search is to conduct search using the subject fields recommended by CNKI, which contain all subjects of an article. Professional dictionaries, subject terms list, bilingual dictionaries, stop words list and other tools are imported in the process of search. Keywords truncation algorithm are used to intercept the documents which have low or micro correlation with subjects.
(2) Keyword search
The keywords include the Chinese and English keywords given in the original text of the documents, as well as the keywords recommended by CNKI after the analysis and calculation of the documents. The keywords recommended by CNKI based on the analysis of the full text combined with professional dictionaries, solve the problem that the keywords given by the document authors are not complete and precise.
(3) Title search
The titles of journals, proceedings, theses and monographic serials are both in English and Chinese. The titles of newspaper articles include eyebrow head, official title and subhead. The titles of yearbooks are the titles of tabs. Patents' titles are the name of patents. Standards' titles are the name of standards in English and Chinese. Achievements' titles are the name of achievements. Ancient books' titles are the volume name.
(4) Full text search
Full text search refers to the search within the full text of the documents, including the title, keywords, abstract, text and reference of the documents.
(5) Author search
The authors of journals, newspapers, proceedings, theses, yearbooks, and monographic serials are both in English and Chinese. Patents' authors are the inventors. Standards' authors are the drafters or main drafters. Achievements' authors are the person-in-charge of the achievements. Ancient books' authors are the authors of the whole books.
(6) The first author search
When there is only one author in an article, the author is the first author. When there are several authors in an article, the author ranking first is identified as the first responsible person for the article.
(7) Corresponding author search
At present, the corresponding authors of the original text of journal documents are indexed, and can be used to search the journal documents. Corresponding authors are the chief heads of a project and the contact persons for articles and research materials.
(8) Author’s affiliation search
The affiliation of the authors of journals, newspapers, proceedings, and monographic serials is the name of the authors' organization given by the original text. The author’s affiliation of theses includes the author's degree-awarding affiliation and the organization the author works in given by the original text. The author’s affiliation of yearbooks includes tab author’s affiliation and chief editor's affiliation. The author’s affiliation of patents is the organisation that files patents. The author’s affiliation of standards is the organisation that releases standards. The author’s affiliation of achievements is the organisation that finishes the achievements firstly.
(9) Fund search
The documents supported by certain fund can be searched according to the name of the fund. The resources types that support fund search include: journals, proceedings, theses and monographic serials.
(10) Abstract search
The abstracts of journals, proceedings, theses, patents and monographic serials are the Chinese and English abstracts of the original text. If the abstract of the original text is not given, part of the text is extracted as the abstract. Standards' abstracts are the scope of standards. Achievements' abstracts are the brief introduction of achievements.
(11) References search
Search the documents for which the references contain search terms. The resources types that support references search include: journals, proceedings, theses, yearbooks and monographic serials.
(12) The CLC number search
All the documents in the same category can be searched through the CLC number search. The classification code of journals, newspapers, proceedings, theses, yearbooks, standards, achievements and monographic serials is the CLC number. Patent CLC number refers to the CLC number of patents.
(13) Literature source search
Literature source refers to the source of documents. The source of journals, monographic serials, newspapers, proceedings and yearbooks is the publication where the literature are published. The literature source of theses refers to corresponding degree-awarding affiliation. The literature source of patents refers to the patentee/applicant. The literature source of standards is the organization that releases standards. The literature source of achievements is the organization that evaluates the achievements.
Search recommendation/guidance
CNKI platform provides intelligent recommendation and guidance in the process of search, and can automatically give prompt according to the entered search terms. Users can select the recommended terms according to the prompt so as to get precise results quickly.
After using the function of recommendation or guidance, users are not allowed to change the recommended terms in the search box, which may result in wrong results or no results.
(1) Intelligent prompt for subject terms
CNKI platform will automatically complement the search terms entered by users. Applicable fields: subject, title, keyword, abstract and full text.
For example, if you enter the word "gene", the hot words begin with "gene" will appear in the drop-down list of the platform. Select the recommended word by mouse (keyboard), and then click "Search" button (press "Enter") or click the recommended word to conduct search.

(2) Author guidance
Enter search terms for search guidance and then select the recommended terms according to needs to precisely determine the author to be searched.
For example, if you enter "Wang Dazhong", and then select the first-level "Wang Dazhong Tshinghua University", you can search all the documents published by Wang Dazhong from Tshinghua University. As long as you precisely determine the author and exclude the authors of the same name, all the documents published by the author can be searched regardless of whether the affiliation of the original text includes Tshinghua University.

If an author has several affiliations, or you need to search all the documents of the author in the previous affiliation and the current affiliation, select several affiliations in the drop-down list. For example, if you want to search the documents published by Li Xingde in linguistics, select all his affiliations to get search results.

If the primary affiliations of two authors are the same and the secondary affiliations are different, select corresponding secondary affiliation to precisely determine the author. For example, if you want to search the articles published by Zhang Huan from the School of Physics, Peking University, select the terms which contain the "School of Physics, Peking University" in the secondary affiliation.

(3) Fund guidance
Enter search terms, and the standard fund names containing the search terms will appear in the drop-down list. Select the fund name you need and use standard fund code for search and precise positioning.
For example, if you enter "natural science", select "National Natural Science Foundation of China" in the drop-down list and click "Search" button. The search results will show all the documents of which the standard fund name is the National Natural Science Foundation of China.

(4) Literature source guidance
Enter search terms, and the standard source names containing the search terms will appear in the drop-down list. Select the name you need and use source code for search and precise positioning. The resources types that support document source guidance include: journals, newspapers, theses, yearbooks and monographic serials.
For example, if you enter "industrial economy", and select the source name you need in the drop-down list, the search results will contain all the documents under the current and former names of the source.

Matching modes
Basic search adopts different matching modes according to the characteristics of search items.
Correlation matching. The search items that adopt correlation matching are: subject, title, full text, abstract, references, and document source. Obtain high relevant search results according to the matching degree of search terms in this field.
Precise matching. The search items that adopt precise matching are: keyword, author, the first author and corresponding author.
Fuzzy matching. The search items that adopt fuzzy matching are: author’s affiliation, fund and the CLC number.
Search in results
Search in results refers to the search within the scope of the previous search results according to the newly entered search criteria.
Enter search terms and click "Search Within Search Results", and the search criteria will appear above the Search Result Area, as shown in Fig. 1.2.1.6:

Search the documents with the subject of "artificial intelligence" firstly, and then search the documents with the source of "computer knowledge and technology" within search results. Click
Search method > advanced search
Advanced search entry
Click "Advanced Search" in the home page to enter the advanced search page (see Fig. 1.2.2.1-1), or click "Advanced Search" in the one-stop search results page to enter the advanced search page (see Fig. 1.2.2.1-2).


Click the tabs in the advanced search page to switch into the Advanced Search, Professional Search, Scholar Search and Sentence Search, as shown in Fig. 1.2.2.1-3.

Features of advanced search
Advanced search supports the logical combination of multiple fields, and can complete more complex search by selecting precise or fuzzy matching modes and search control methods so as to obtain desired search results.
In multi-field search, the order of operations is from the top to the bottom.
Search Area
In the Search Area, the upper half part is the Search Criteria Input Area, and the lower half part is the Search Control Area.
(1) Search Criteria Input Area
The default option is three search boxes of the subject, author and document source. Search items, the logical relation between them (Fig. 1.2.2.3-1) and the matching method of search terms (Fig. 1.2.2.3-2) are free options:


Click![]() and
and![]() after the search box to add or delete search items. A combination of up to 10 items is supported.
after the search box to add or delete search items. A combination of up to 10 items is supported.
(2) Search Control Area
Results are controlled by criteria filtering and time selection.
Conditions are: publishing mode, fund documents, time range and expanded search. See Fig. 1.2.2.3-3.

Chinese and English expansion is performed by default. If it is not required, please uncheck it.
Search items
In advanced search, various search items are provided to meet different requirements. Items are: subject, keyword, title, full text, author, the first author, corresponding author, author's affiliation, fund, abstract, reference, Chinese Library Classification (CLC) and document source. For detailed information about the items, see 1.2.1.3. Search items.
Database Switch Area
The Database Switch Area is at the bottom of the page of advanced search. Click the name of the database to switch to a single database.

Literature navigation
The navigation of classified literature is collapsed by default. To narrow search range, click to expand the navigation and check the categories needed. Navigation for 168 special subjects in general database is a classified system independently created by CNKI based on Chinese Library Classification. Besides the navigation for 168 special subjects, the special navigation in a single database is provided for yearbooks, standards and patents.
Search recommendation/guidance
It is similar to the function of intelligent recommendation and guidance of one-stop search. But the main differences are: in advanced search, first, for content items such as subject, title, keyword, abstract and full text, synonyms, hypernyms, hyponyms or related words are recommended; second, the icon of recommendation and guidance is displayed on the right side of the page. Check the function to search, and the result will contain all documents of search terms or checked terms.
For example: after "artificial intelligence" is input, related words such as "machine intelligence" and "decision-making system" are recommended for checking.

Matching modes
Except that subject is provided only with correlation matching, others are all provided with two matching methods, precise or fuzzy.
On the one hand, for the precise matching of title, abstract, full text and reference, search terms are matched as a whole based on the search item, the accurate results of which contain complete search terms. For their fuzzy matching, it is a matching result of segments of search terms based on the search item.
On the other hand, for the precise matching of keyword, author, organization, fund, CLC and literature source, search terms are matched in full accord. For their fuzzy matching, it refers to the inclusion of search terms.
Selection of word frequency
In full text search and abstract search, word frequency is used to optimize search results.
After the selection of word frequency, the search result is documents which contain larger or the same numbers of search terms within the full text or the abstract.
Search in results
Advanced search supports search within search results. After execution, search criteria are displayed above the Search Result Area, and the search criterion is connected with the former one with an "AND".
For example: after the search of "artificial intelligence", search "robots" within search results, and see the search criteria in Fig. 1.2.2.10:

Collapsed or expanded Search Area
After the advanced search, the Search Area only displays the search box of the first line to reduce the space and highlight the result. Click the button of expansion to display the whole search Area.

Search method > scholar search
In the advanced search page, switch the tag to scholar search.
In scholar search, literature published by an author can be searched by inputting the author's name and affiliation. The function and operation of scholar search are basically the same as advanced search.
Search method > sentence search
In the advanced search page, switch the tag to sentence search.
By two search terms, the full text is searched for a sentence that contains both terms and find answers to questions.
Empty search is not supported in sentence search. Two search terms are necessary in the search within a sentence or a paragraph.
For example: search the document where "artificial intelligence" and "neural network" are in the same sentence.

See the search result below. Sentence 1 and 2 are originals, and "source" contains the title of the document.

The search via combination of the same sentence or paragraph is also supported. For example, search the full text for a sentence that contains both "data" and "mining" and another sentence contains both "computer" and "network", and see Fig. 1.2.4-3:

In the document searched, there is a sentence contains both "data" and "mining", and another contains both "computer" and "network". For example, the result below does not contain a sentence with all 4 terms (Fig. 1.2.4-4).

Search method > professional search
Profile of professional search
In the advanced search page, switch the tag to professional search.
Professional search is used in library and information science for novelty search and information analysis by building search strategies of operators and search terms.
General process of professional search: a general search strategy is built by search fields, and a complex search strategy is built by the relational operator between fields and the search value resolution operator.
General formula of professional search: <field><matching operator><search value>

Search field
Retrievable fields provided in the general database are as follows: SU=subject, TI=title, KY=keyword, AB=abstract, FT=full text, AU=author, FI=the first person responsible, RP=corresponding author, AF=affiliation, JN=journal (document source), YE=year, FU=fund, CLC=Chinese Library Classification, SN=ISSN, CN=Chinese Number, IB=ISBN, CF=citation frequency.
Matching operator
| Sign | Function | Applicable field |
|---|---|---|
| = | = ‘str’ represents the search of records equal to str | KY、AU、FI、RP、JN、AF、FU、CLC、SN、CN、IB、CF |
| =‘str’represents records contain complete str | TI、AB、FT、RF | |
| % | % ‘str’ represents records contain complete str | KY、AU、FI、RP、JN、FU |
| %‘str’ represents records contain str and participles of str | TI、AB、FT、RF | |
| %‘str’ represents records of consistent matching or string matching with the former part | CLC | |
| %= | %= ’str’ represents relevant records matching str | SU |
| %= ’str’represents records contain complete str | CLC、ISSN、CN、IB |
Examples:
(1) Precise search of the document contains the keyword "data mining": KY = data mining.
(2) Fuzzy search of the document with the abstract which includes "computer teaching": AB % computer teaching. The search result is the document with the abstract which includes "computer" and "teaching" regardless of order and distance.
(3) The search of the document with a subject related to "big data": SU %= big data. In subject search, "%=" is recommended.
Comparison operator
| Sign | Function | Applicable field |
|---|---|---|
| BETWEEN | BETWEEN (‘str1’ , ’str2’) represents the matching of the value between str1 and str2 | YE |
| > | Greater than | YE CF |
| < | Less than | |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
Examples:
(1)YE BETWEEN ('2010', '2018'), search the document published between 2010 and 2018.
(2)CF > 0 or CF >=1 , search the document which has been cited.
Logical operator
It is applied to logical operation between fields.
| Sign | Function |
|---|---|
| AND | Logic "and" |
| OR | Logic "or" |
| NOT | Logic "not" |
Examples:
(1) Search articles published by Qiu Junping with the keyword which contains "knowledge management". Formula: KY = knowledge management AND AU = Qiu Junping.
(2) Search the document with the subject related to knowledge management or information management. Formula: SU %= knowledge management OR SU %= information management.
(3) Search articles with the title which contains "big data", excluding those with "big data set". Formula: TI = big data NOT TI = big data set.
(4) Search articles published by Qian Weichang when he was in Tshinghua University or Shanghai University. Formula: AU = Qian Weichang AND (AF = Tshinghua University OR AF = Shanghai University).
(5) Search articles published by Qian Weichang with a title or an abstract contains "physics" when he was in Tshinghua University. Formula: AU = Qian Weichang AND AF = Tshinghua University AND (TI = physics OR AB = physics).
Notes:
(1) Various fields are combined by AND, OR and NOT. Formula is constructed as follow: <field><matching operator><search value><logic operator><field><matching operator><search value>, And remember the space before and after "AND" "OR" and "NOT".
(2) Logic search formula is free to combine, but precedence is specified by "()", the half-width parentheses in the English mode.
Composite operator
The composite operator is mainly applied to complex and efficient formula of search keywords.
| Sign | Function |
|---|---|
| * | ‘str1 * str2’: containing both str1 and str2 |
| + | ‘str1 + str2’: containing both str1 and str2 |
| - | ‘str1 -str2’: containing str1 or str2 |
Examples:
(1) Search the document with the full text which contains both "catalyst" and "reaction rate”: FT = catalyst * reaction rate.
(2) Search the document with keywords which contain "aluminium alloy “or "titanium alloy”: KY = aluminium alloy + titanium alloy.
(3) Search the document with keywords which contain "big data" but exclude "artificial intelligence”: KY = big data - artificial intelligence.
Notes:
(1) Within one field, multiple search values can be combined by "*", "+" and "-".
(2) The order of operations of a composite operator combination can be changed by "()".
Location operator
It is applied to logical operation between fields.
| Sign | Function | Applicable field |
|---|---|---|
| # | 'STR1 # STR2' : a sentence contains both STR1 and STR2 | TI、AB、FT |
| % | 'STR1 % STR2': a sentence contains both STR1 and STR2, and STR1 is before STR2 | |
| /NEAR N | 'STR1 /NEAR N STR2': a sentence contains both STR1 and STR2, with no more than N words between them | |
| /PREV N | 'STR1 /PREV N STR2'' : a sentence contains both STR1 and STR2, and STR1 is before STR2 with no more than N words between them | |
| /AFT N | 'STR1 /AFT N STR2': a sentence contains both STR1 and STR2, and STR1 is after STR2 with more than N words between them | |
| $ N | 'STR $ N’: STR appears at least N times | |
| /SEN N | 'STR1 /SEN N STR2' : a paragraph contains both STR1 and STR2, and the number of sentences between them no more than N. | |
| /PRG N | 'STR1 /PRG N STR2' : the result contains both STR1 and STR2, with no more than N paragraphs between them | |
| $ N | 'STR $ N' : STR appears at least N times |
Examples:
(1) FT = 'artificial intelligence # recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a sentence.
(2) FT = 'artificial intelligence % recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a sentence, and "artificial intelligence" is before "recommendation algorithm"
(3) FT = 'artificial intelligence /NEAR 10 recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a sentence, with no more than 10 words between them.
(4) FT = 'artificial intelligence /PREV 10 recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a sentence, and "artificial intelligence" is before "recommendation algorithm" with no more than 10 words between them.
(5) FT = 'artificial intelligence /AFT 10 recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a sentence, and "artificial intelligence" is after "recommendation algorithm" with no more than 10 words between them.
(6) FT = 'artificial intelligence /SEN 1 recommendation algorithm'. Search the document where the full text contains both "artificial intelligence" and "recommendation algorithm" in a paragraph, with no more than 1 sentence between them.
(7) FT = 'publication /PRG 5 laws and regulations'. Search the document where the full text contains both "publication" and "laws and regulations", with no more than 5 paragraphs between them.
(8) FT = 'big data $5'. Search the document where the full text contains more than 5 words of "big data".
Notes:
(1) The search value and its operator should be enclosed by half-width apostrophes in the English mode.
(2) In a single field at one time, "#, %, /NEAR N, /PREV N, /AFT N, /SEN N and /PRG N" can only connect 2 search values.
Search Result > resource type
All resource types supported are displayed resource horizontally. After the search, the number of documents that meet the search criteria is displayed below each resource type to show the distribution. Click to learn documents of any resource type.

Search Result > language
Click "Chinese" or "foreign language" to view documents in various languages. Click "general database" to back to the mixed results.

Search Result > single database search
When a single database is selected, the Search Area above displays search items of this single database. For example, when "journal" is selected, the search items include subject, journal name and DOI. See Fig. 1.3.3-1.

Click the search button above to enter the single database search within "journal". In the single database search, results are displayed at the upper right corner of the Search Result Area.

Search Result > search criteria display
At the upper left corner of the Search Result Area, search scope and search criteria are displayed, and customization function is provided to view search history and search formula.

Search Result > subject customization
Log in a personal account to click the "subject customization" to add the current search formula to the personal study. Keep abreast of the latest achievements and developments in the areas of interest.
Search Result > search history
Click "search history" to view the history. The last 10 records can be viewed if the user is not logged in. On the search history page, click the search criteria to view the results directly.
Search Result > group filtering
On the left of the Search Result Area, Group Filtering Area provides different angles and supports combinations of multiple criteria to search high-quality documents in the search result quickly and accurately.
Except groups of science and social sciences, each group displays two categories by default. For all categories, click the drop down arrow ![]() , on the group tag.
, on the group tag.
After checking the group, click the left OK button to perform filter; click the right reset button to clear all checks.

Group segmentation
Research level is segmented into science & technology and social sciences, allowing users (knowledge service objects) to search for documents based on research fields.
Subjects are segmented to main subject and secondary subject, according to the share of one subject term making up in the documents.
Authors and institutions are segmented to China and Foreign Countries, referring to author/institutions of Chinese documents and that of foreign documents.
Group contents sorting
Authors are listed in descending order by H index. Authors with high H index rank ahead to help select authoritative literature.
Chinese and other language journals are listed together in descending order by CI index, facilitating selection of valuable documents based on journals’ quality.
Grouping and visualization
All groups except scientific & technology and social science allow visualization analysis, to directly reflect the documents of certain groups in search results. Click ![]() to see the visualization image as shown in Fig. 1.3.7.3.
to see the visualization image as shown in Fig. 1.3.7.3.

Search Result > Integration of horizontal resource types and vertical group filtering
Horizontal Resource Types Area and vertical Groups Area form a knowledge service matrix, enabling users to find needed documents quickly and effectively.

For example, searching for subject “artificial intelligence” can get results showed above. Click “Journals” to see documents with the subject of “artificial intelligence.” Groups Area on the left side is now composed of different journals for further filtering.

Select the journal Cancer Letters. The number of results will be shown at the top right corner of the Search Result Zone.

Search Result > tendency chart of published years
Tendency Chart of Published Years sits on the right side of the page. Users can click the floating icon to see the chart of research results. It directly shows the published years of literature.

Input the starting and ending years under the chart, click the “Filter” and get search results of this period.
Search Result > sorting
Users can sort search results in terms of publication date, relevance, citation counts and download counts as needed.

Full-text search is sorted by relevance by default; the highest relevance appears first. Results of other search methods are sorted by publication date by default; the latest research results and directions appear first.
Search Result > The number of results
Select the number of results showed on each page.

Search Result > display modes
Search results can be displayed in Detail Mode or List Mode.

Detail Mode
Detail Mode shows bibliographical information in detail, allowing users to find right documents. The page is divided into two zones: the left one is for bibliographical information and the right one for operation.

(1) Bibliographical information
It shows title of article, author name, author affiliation, resource type, document source, publication date, citation counts, download counts, abstract and keywords.
Click the title of article to enter the document knowledge network node; click the name of document source, such as journal title, to enter the publication detail page; click keywords to visit the keywords knowledge network node.
Author names and affiliations will correspond to journals, proceedings and monographic serials. Name and affiliation of the first author are displayed by default. Users can see names and affiliations of all authors by clicking the expand arrow. Click the regulated name or affiliation of author can jump to the author or institution knowledge network node.

(2) Function area
Users can favorite, read, download and cite single literature.
Log-in is required to favorite literature, which can be found in “Favorites” of “Personal Study.”
Users can log in to read html articles after related processing or read un-processed articles online.
Users can download documents with accounts having such privilege. Users can visit foreign cooperative database to download documents through the link![]() ,attached to documents (journals and books).
,attached to documents (journals and books).
Users can cite documents by copying their citation formats. There are three formats: users can directly copy and paste the default national standard format. For the other two, users need to click the words to copy them. When citing single document, there is no need to tick and export them, which is more convenient.

List Mode
List Mode is simple and clear, easy for quick viewing and location. It displays search results in lists, offering key information such as title of article, author name, document source, publication date, citation counts and download counts. Operation and jumping regulations of functions such as download and reading in the List Mode are same as that in the Detail Mode.

Search Result > literature management
Users can deal with the selected documents in Document Management Center. For example, they can export documents, generate search reports, conduct visualization analysis, and read the documents online.


Users can also click the “Export and Analyze” icon to visit the corresponding operation interface.

Literature Management Center
Display all selected literature in lists by groups based on different search conditions; display entries of selected literature by groups based on different search conditions.
Users can re-select the already selected literature, and then export bibliographical information and generate search reports of these newly selected literature.
Users can delete any one of the selected literature by clicking the “✖” icon on the right side; delete multiple selected literature by ticking the check boxes on the left side and clicking the delete button.

Export literature
Enter the Bibliographic Information Export page through the Search Result page or Document Management Center page. Users can export literature in different formats as listed in the following figure. It is displayed in the GB/T 7714-2015 format by default.

Formats and functions of GB/T 7714-2015 Format Citation, CAJ-CD Format Citation, and Novelty Search (Citation Format) are the same.
(1) Selected literature
Users can return to the selected literature page (Literature Management Center) to re-select entries of the selected literature. Please refer to 1.3.13.1 Literature Management Center.
(2) Custom fields selection
Users can select custom fields in Novelty Search (User-defined Citation Format) and User-defined Format.
Users cannot change the selected state of default fields, but can reset the state of custom fields. After the state of the latter is changed, users can click “Preview” to see the new output results at Result Preview Area.

(3) Preview
The button do not work when there is no custom fields.
Users can click the button to preview the new results of custom fields.
(4) Export/Copy to Clipboard/Print/xls/doc
Export bibliographical information of the selected literature in the “Literature export format” and save it.
xls. refers to Excel Literature and doc. Word Literature. CNKI E-Study, Refworks, EndNote, NoteExpress and NoteFirst have no “xls” and “doc” buttons.
(5) Sorting
It can display the literature in terms of publication date and citation counts in ascending/descending order.

Generate search report
Search report generated mainly includes search conditions, search statistical statement, search evaluation, search report executor and save/print search report.

Visualization analysis
(1) Cross-citation network
Cross-citation network analysis is based on the citation network composed of Literature reference and citation, aiming to help users find valuable literature from the references and cited literature.

-
Information display
Types of Information Display include showing titles of journals and citation counts of the selected literature; showing keywords; showing author names; showing Literature sources. Different types decide certain node’s contents of Information Display.
-
Node filtering
Reference conditions of Node Filtering include citation counts, relationship strength, reference node and citation node. Users can change the default citation counts to others in the drop-down list.
Based on the citation counts filter, users will not see literature that citation counts do not meet the default value.
Relationship strength refers to the number of lines directly connected to the current node. It reveals the number of reference nodes and citation nodes among all nodes in the current relationship network. The filter represents the connection and relational degree of the current node with other nodes in this Literature network. Through relationship strength, users can find node literature important in the current Literature network.
Reference node refers to the number of lines from the current node to other nodes, which means the number of references of the current Literature in this Literature network. However, that number does not equal to the actual number of references of the node Literature.
Citation node refers to the number of lines directing at the current node, which means the number of literature in this Literature network that has cited the current Literature. However, that number does not equal to the actual citation counts of the current node Literature.
-
Relationship analysis
It includes single-layer relationship and multi-layer relationship. The default “Please Select” means that no node and link directly connected with the current node will display when the node was clicked. When selecting the single-layer relationship, users will see only one relationship; when selecting the other, users will see the reference citation relationship simultaneously. Users should combine types of Information Display with that of Relationship types.
Relationship types include reference citation, references, and citing literature, from which users can select. If selecting the reference citation relationship, multi-layer relationship and any nodes, users will see all nodes and links sharing the reference citation relationship with the current node and other nodes will turn grey. If the references or citation literature relationships are selected, the results are similar: only nodes of the corresponding relationships will be displayed.
-
Additional remarks
Frequency statistics hidden on the right of the visual figure includes keyword frequency, author frequency, the number of literature of different years and sources (publication sources). Clicking all words is to select highlights. Resetting the filtering conditions can be realized by selecting all node filters. For example, if users select one keyword, they can see only node literature containing that keyword.
In the Relationship Analysis, parameters of relationship play main role in displaying information. If users select Reference Citation and single-layer relationship at the same time, the information displayed will include references and citing literature, namely a result of multi-layer relationship. Thus, users can set parameters of relationship only in Relationship Analysis.
Lines in this figure have arrows and directions of these arrows stand for Literature citation relationship.
Results of bibliographic coupling analysis and co-citation analysis will be displayed below. In other words, literature and coupled literature/literature and co-cited literature are displayed. literature here reflect relationships among nodes and lines in the Literature network.
(2) Keyword co-occurrence network
Keyword co-occurrence network is built with keywords as nodes and co-occurrence relationship as the foundation. Through keyword co-occurrence, users can analyze subjects, namely main research contents, of the selected literature. Co-occurrence relationship describes the relation between two or more keywords existing in the same Literature.
Select literature to be analyzed (less than 200 pieces) on the Search Result page as the analysis object. Each node in the keyword co-occurrence network represents one keyword.
Size of the node is positively related to keyword frequency. The more frequently a keyword appears, the larger the node is. Keyword is displayed on the node by default (enlarge the figure to see it). Double click the keyword to jump to its keywords knowledge network node. Thickness of lines linking two nodes represent their co-occurrence frequency. Mark one group composed of closely-related nodes with the same color.

-
Relationship analysis
Users can select “Nearby Nodes” to get corresponding response effect. Under the default “Please Select,” there is no node-clicked effect. Under the “Nearby Nodes,” nodes directly connected to the clicked node will be displayed. In other words, users can get keywords sharing direct co-occurrence relationship with the selected keyword.
-
Node filtering
Node Filtering condition is occurrence frequency. Users can set the threshold value through the selector or by inputting number. Input the number N; click “Filter” to get keywords appearing more frequently than the threshold value. Values of N should be decided according to the total number indicated in the node information. Click “All” to reset the filtering condition. It’s worth noting that the occurrence frequency refers to the number displayed in the node information when being pointed by the mouse pointer. It means the total number that the keyword appears in the selected literature, which differs from co-occurrence frequency.
Year analysis
Display keyword occurrence frequency by years. Its function is similar to selection by publication year of literature with certain keywords. Users can understand how research subjects of the selected literature change and develop during these years.
-
Cluster analysis
Cluster analysis focuses on occurrence frequency of certain keywords in one Literature, showing connection strength among keywords. Cluster analysis needs to calculate distance between nodes and group them to clusters.
The default number of clusters is 3, which can be adjusted from 1 to 6. It means that based on connection strength, the keywords can be grouped to 6 clusters at most. The number of clusters should be adjusted according to the display effect.
Tick the “Show the Central Node” to display the keyword on the central node of one cluster.
-
Additional remarks
Foundation of the keyword co-occurrence network analysis is auto-tagged keywords, instead of self-tagged ones. The former is more normative and accurate in showing the subject than the latter.
Central node keyword is a result of pre-calculation. When adjusting the number of clusters to the number of groups, the central node keyword will be displayed. It is possible that one group has many central node keywords.
(3) Author cooperation network
Author cooperation network is about authors’ cooperation relationship in one set of literature. Authors of one Literature are cooperators, namely they share a cooperation relationship. In the figure of author cooperation network, they are nodes connected by lines.
The author name will be shown on the node. Users can double click the node to visit the corresponding author knowledge network node. The size of node represents the number of the author’s published papers, which can be searched in CNKI (author represented by author code). Thickness of the line connecting two nodes stands for cooperation frequency of the two authors.

-
Relationship analysis
Users can set node-clicked effect in the Relationship Analysis. Under the “Please Select,” there is no effect. Under the “Nearby Nodes,” author nodes sharing direct cooperation relationships with the clicked node will be displayed.
“Show the Co-occurrence Frequency” is not ticked by default. Users can tick it to see co-occurrence frequency on the line connecting two nodes, which shows how many times the two authors cooperate in the selected literature.
-
Node filtering
Users can set the threshold value of occurrence frequency through the selector or by inputting number. Input the number N; click “Filter” to get authors with the number of cooperation greater than N (not including the ones equal to N). Values of N should be decided according to the actual number of co-occurrence frequency in Relationship Analysis. Click “All” to reset the filtering condition.
-
Year analysis
Display cooperation relationships by years. The number of published papers will be shown in the brackets on the right of node author name. Users can understand author cooperation in different years.
-
Others
When users move the mouse pointer to the node, they can see information like “Author (author affiliation) [the number of published papers].” It’s worth noting that “the number of published papers” refers to the total number of papers that can be searched in CNKI.
Online reading
Different from preview of single Literature at the Search Result page, it refers to online reading of the multiple selected literature.

Search Result > relevant search recommendation
Relevant search recommendation is available below the search results. Relevant search will recommend words related to the one input by users, including research subjects and famous scholars, as reference of systematic academic research.

Relevant search will recommend 14 subject terms related to search terms at most. Users can click one subject term, and the system will perform subject search with such subject term as the search term.
The system will recommend 14 experts and scholars with the highest G index. Users can click their names to visit the author knowledge network node.
Search Options
The function, search settings, offers personalized services concerning general database search. Users can perform preference setting based on personal habits to facilitate operation.
It is available for general database search only, located at the head of basic search Result page and Advanced Search page.

Users can set cross-database search scope and search result format.
Permanent saving of settings needs account log-in. If users close the browser or do not perform any operation on the platform in 20 minutes, the settings will return to the system default.
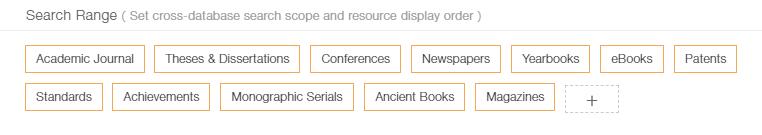
Search Options > Set cross-database search scope
Set resource types and display order for cross-database search.

All types of resources participating in general database search will be shown by default. A cross will show at the upper right corner of the name of one resource ![]() ,when pointed by a mouse pointer. Users can delete the resource type by clicking that cross. As a result, general database search will not search for literature in that type. Users can click
,when pointed by a mouse pointer. Users can delete the resource type by clicking that cross. As a result, general database search will not search for literature in that type. Users can click![]() to add resource types needed to be included in the cross-database search.
to add resource types needed to be included in the cross-database search.
By dragging the resource types, users can change the display order of search results.
For example, if users include Journals, Newspapers and Proceedings in general database search, the results will be displayed in the order of Proceedings, Newspapers and Journals as follows:

Click “Save,” refresh the page and search for “artificial intelligence.” The search results are shown as:

Proceedings, journals and newspapers will be put at the forefront in sequence, while other resources will not be included in the general database search. The number of literature will not be displayed below the resource names.
Search Options > Set search result format
The format includes the default number of records displayed, default display mode and default sorting.

Refresh the page after setting, and the number of records displayed, display mode and sorting will be displayed as per default options.
Knowledge Network Node
Knowledge network nodes mainly include the Literature knowledge network node, author knowledge network node, institution knowledge network node, discipline knowledge network node, fund knowledge network node, keywords knowledge network node and the publication knowledge network node.

Knowledge Network Node > literature knowledge network node
Literature knowledge network node entry: Search result > Titles on Literature list, i.e. where there is a link to a Literature title, there will be an entry to the Literature knowledge network node upon a click.
Basic information
The Literature knowledge network nodes for journals, monographic serials, proceedings and academic dissertations display their pages in three columns, listing the contents, bibliographic and abstract information and citing literature from left to right. Contents and citing literature can be folded or unfolded, and the two sides are folded by default when there is no content on the page. The knowledge network nodes for other single database products will be set in one column.

(1) Bibliographic and abstract information
A Literature knowledge network node has such basic information as the title, author, institution, abstract, keywords, DOI, fund, collection, subject, class number, download frequency, Literature source, contents, in-text pictures, citing literature, etc. Click the links to the above information to enter corresponding knowledge network nodes. Each single database product contains different knowledge node information in its knowledge network node.
(2) Contents and In-text Pictures
Contents and in-text pictures will be displayed on the left side. Contents refer to the different sections or chapters shown in a list in an article. It helps users to understand the article structure and the framework of content, to learn the brief outline of the article or to tell the reading value of the Literature. In-text pictures: 6 thumbnails of illustrations will be displayed for an article, and a click will offer details about the illustrations; when there are more than 6 thumbnails, click “more” to skip to view all pictures illustrated in the corresponding Literature.
(3) Citing literature
Citing literature will be displayed on the right side. The total citation frequency of the node literature will be highlighted. 10 citing literature will be displayed in the sequence of the H-index of the first author. The content displayed includes the citing authors’ names and the H-index of the first author. Click the author to open the knowledge network node of the corresponding article; and click “more” below the list of citing literature to skip to the citing literature in the “knowledge network” of the node Literature.
Citing literature refer to the literature citing the node Literature as a source. They represent the continuance, application, development or evaluation of the study of the node Literature. Citation frequency is an important measure of the influence of academic writings. Higher citation frequency suggests, to some extent, higher value of a Literature; if a Literature is cited by many authors with high H-indexes, it may be regarded as authoritative to a certain extent. Citing literature and the information of the citing authors are the reference for readers to tell the value of a Literature.
Download and reading
CAJ download: Users can log in to download the files to their local host and view the literature via CAJViewer.
PDF download: Users can log in to download PDF files to their local host.
HTML reading: Users can log in to read the literature in HTML format online. It is applicable to journals, newspapers and proceedings.
Mobile phone reading: Users can download CNKI Express and scan the QR codes of the literature to open the files on their mobile phones, where the downloading, citing and reading of the literature are available.

Operation of node literature
Click the citing button ![]() in
in ![]() , and three citation formats will pop up. The default format is GB/T 7714-2015, which can be copied. Click more citation formats to enter the Literature management center; personal accounts can click the citation tracking button
, and three citation formats will pop up. The default format is GB/T 7714-2015, which can be copied. Click more citation formats to enter the Literature management center; personal accounts can click the citation tracking button![]() to create citation tracking, and click the icon again to enter the citation tracking in the personal study; personal accounts can click the favorites button
to create citation tracking, and click the icon again to enter the citation tracking in the personal study; personal accounts can click the favorites button![]() to collect literature and click the icon again to enter the citation tracking in the personal study; click the share button
to collect literature and click the icon again to enter the citation tracking in the personal study; click the share button ![]() to copy the link or share the Literature to WeChat or Weibo.
to copy the link or share the Literature to WeChat or Weibo.
Subject network
A Literature subject context diagram, centered on the node Literature, diagrammatizes the starting point of research, the study source, study branch and study direction of relevant subjects of the node Literature.
Literature subject context diagrams display the subject terms of the node Literature, and a subject context diagram can display 9 subject terms at most. The starting point of research is the subject term of secondary references; study source is the subject term of references; study branch is the subject term of citing literature; and study direction is the subject of secondary citing literature. They will be selected by the occurrence frequency of the subject terms from the most to the least. 10 entries will be displayed at most. Move the mouse to the subject term to show the title of the source Literature of the subject term; and click the title to link to the knowledge network node page of the Literature.

Citation network
The citation network contains: Secondary references, references, citing literature, secondary citing literature, coupled literature and co-cited literature. Definitions of these literature: References reflect the study background and basis of the node Literature; secondary references are the references of the references of the node Literature and further reflect the study background and basis of the node Literature; citing literature are those citing the node literature and reflect the continuance, application, development or evaluation of the study of the node Literature; secondary citing literature are the citing literature of the citing literature of the node Literature, and they further reflect the continuance, application, development or evaluation of the study of the node Literature; coupled literature have the same references and the same study background or basis with the node Literature; co-cited literature and the node Literature are both cited by the same literature, as shown in Fig. 1.5.1.5-1..5.1.5-1。

The number of each kind of Literature will be marked behind the title and given in brackets, as shown in References (13);
Click the citation type in the citation network diagram, such as references, and the type of literature will display below the diagram. Databases involved include China Academic Journal Network Publishing Database, China Master’s Theses Full-text Database, Springer journal database and foreign language bibliographic database.

Relevant literature recommendation
(1) Similar literature
Recommend literature similar to the node Literature based on collaborative filtering algorithm.

(2) Readers’ recommendation
It recommends based on relevant logging data users to download the literature downloaded by other readers.

(3) literature supported by the same fund

(4)Associated author
Associated author include the authors of references and citing literature, as shown in the figure below:

Knowledge Network Node > author knowledge network node entry
Author knowledge network node entry
Search result > author; Literature knowledge network node > author; associated author; relevant author, etc. i.e. where there is a link to an author, there will be an entry to the author knowledge network node upon a click on the author’s name.




Author knowledge network node entry page
An author knowledge network node page lists an author’s basic information, other authors of the same name, sectors of the author’s concern, the author’s works, the author’s supervisors, co-authors, funds obtained, students supervised by the author, etc. to provide rich information for readers.

Knowledge Network Node > institution knowledge network node
Institution knowledge network node entry
Literature Knowledge Network Node > Institution

Institution knowledge network node page
An institution knowledge network node contains the profile of an institution, its major authors, publications, major disciplines, most-cited literature, most-downloaded literature, journal literature, foreign journal literature, newspaper literature, proceedings, doctoral or master’s dissertations, subordinates and relevant institutions.

Knowledge Network Node > publication knowledge network node
Details are shown in the publication knowledge network node (detail page of journal) of each single database product.
Knowledge Network node > keywords knowledge network node
Keywords knowledge network node entry
Literature knowledge network node > Keywords:
Author knowledge network node > Sectors of the author’s concern

Keywords knowledge network node page
A keywords knowledge network node contains the explanations of the keywords, analysis on attention index, key literature, relevant literature, discipline distribution, etc. Keywords knowledge network nodes provide readers literature and content relevant to keywords and enable them to quickly find the Literature resources they need.

Knowledge Network Node > discipline knowledge network node
Discipline knowledge network node entry
Literature knowledge network node — institution > Institution knowledge network node — key disciplines > Discipline knowledge network node

Discipline knowledge network node page
A discipline knowledge network node contains function modules such as attention index analysis, discipline literature (e.g. journals, doctoral and master’s dissertations and proceedings), relevant authors and relevant institutions.

Knowledge Network Node > fund knowledge network node
Fund Knowledge Network Node Entry
Literature Knowledge Network Node > Fund

Fund knowledge network node page
A fund knowledge network node page contains the introduction to a fund, most-cited literature of the fund, most-downloaded literature of the fund, journal literature supported by the fund, key result sectors, major authors supported by the fund and major institutions supported by the fund.

Login and Register entry
Entry 1: Navigation bar

Login page:A login window popping up from the bottom of the navigation bar. The options include common login, IP login and log in with a partner website account.

Register page:A sign up interface. Direct login with a partner website account is also available.

Entry 2:
Search result > Download or Read the article in HTML:
Literature knowledge network node > Read the article in HTML or download:
When the user visits the domain name of the personal study, https://oversea.cnki.net/KPC


Login page:A new label page. The options include common login, IP login and log in with a partner website account. The Registeris the same as the sign up interface on the home page.

Entry 3: A login page will pop up at the current page when the user tries to read beyond the free page online.

Personal Library > personal library entry
The personal library is a Literature management service for individuals; therefore, a login with personal account is required to access the service.
Entry 1:CNKI home page Login to the account and click the account name to enter the personal library.

Entry 2:Page head personal library entry

Entry 3:Personalized homepage Link entry to personal library module

Entry 4:Personalized Homepage - Follow -Subscription search type, search history and download history; click “more” to enter the corresponding page of the personal library.
Entry 5:Favorites button. Click the Favorites button and enter personal library - Favorites page to view the literature or publications collected before.
Entry 6:Citation tracking button. Click the citation tracking button and enter personal library - Citation tracking page to view the literature that have been put in for citation tracking.
入口7:Subject customization. Enter personal library - Subscriptions page to view your subscriptions after a subject customization.
Personal Library > literature search
The personal library offers a rapid Literature search service. The default search method is to search in the general database based on the subject.

Personal Library > favorites
Papers favorites
Papers favorited on the personalized homepage, search result page and knowledge network nodes are displayed at the papers module.

Relevant operations:
- Click the title of the Literature collected to enter the Literature knowledge network node page.
- Tagging: Click
 to tag the papers so that the user can view the papers grouped by tags.
to tag the papers so that the user can view the papers grouped by tags. - Download: Click
 to download the literature favorited.
to download the literature favorited. - Exporting/references: Click
 to export references in different formats.
to export references in different formats. - Create citation tracking: Click
 to view how many times the thesis collected has been cited by other literature.
to view how many times the thesis collected has been cited by other literature. - Delete: Click
 to delete the papers favorited.
to delete the papers favorited. - Share: Click
 to copy the link or share the papers favorited to WeChat or Weibo.
to copy the link or share the papers favorited to WeChat or Weibo.
Publication favorites
Users can view the publications favorited at the publishing source navigation page on “Favorites - Publishing Source”. Click the title or picture of the publication to enter the publishing source navigation page which will display details of the publication.

Personal Library > my history
Personal search, download and view histories will be recorded for a personal account. Users can also view the my history by logging into different devices.
Search history

(1) User behavior statistics
Each user’s accumulative searches, comparison with other users and daily average searches are collected weekly or monthly.
(2) Search history information
Search histories are arranged in reverse chronological order. Click the search strategy to enter the search result page which will show the search result of the search strategy; click![]() to customize the search strategy for the search history; click
to customize the search strategy for the search history; click![]() to delete the search history.
to delete the search history.
Download history
Download histories are arranged in reverse chronological order. The operations for literature in this part are the same as that in “1.7.3.1 Papers”.

View history

Browsing histories are arranged in reverse chronological order. The operations for literature or publications in this part are the same as that in “1.7.3 Favorites”.
Personal Library > my subscription
The user’s customized search type can be found at personal library - Subscriptions. There are 3 approaches to subject customization:
(1) search result page: Customize the search strategy by the subject customization button;
(2) personal library - My History - “Subscription” button in Search History;
(3) personal library - My Subscription, “Add” a search type subscription button.
Operations for literature in this part are the same as that in “1.7.3.1 Papers”

Personal Library > citation tracking
A citation tracking to a paper enables the user to timely learn how many times the paper has been cited by other literature.

Citation tracking setting
Set the method and update frequency of citation tracking.
Citation tracking status
Revise the status of citation tracking; delete unnecessary citation tracking for literature.
Personal Library > my achievement
My Achievement

This part displays personal information and the statistics of personal achievements. Operations for literature in this part are the same as that in “1.7.3.1 Papers”.
Push Achievement

Achievements can be pushed as per push conditions. Users can click![]() to claim their own achievements here and check them at the My Achievement page.
to claim their own achievements here and check them at the My Achievement page.
Push conditions setting
Click![]() to edit the push condition.
to edit the push condition.
Personal Library > recycle
The recycle bin stores the content deleted from Favorites - Papers, Favorites - Publishing Source, My Subscription, Citation Tracking and My Achievement. Users can recover, completely delete them here.

Personal Library > user management

Click “User Management” to skip to My CNKI page and edit the user information.
Personalized homepage entry
Entry 1:Click the names of the single databases below the Literature search box at the CNKI home page to enter the home page of each single database.

Entry 2: Input the url to enter the corresponding web page, such as the url of the journal database:https://oversea.cnki.net/kns?dbcode=CJFQ
Single Database > Journal Database
Journal search
(1) Basic search
Click Advanced Search to skip to the advanced search page of the journal database. Details are shown in “1.2.2 Basic search”.

(2) Advanced search
Click Advanced Search to skip to the advanced search page of the journal database. Details are shown in “1.2.2 Basic search”.

(3) Professional search
Click Advanced Search to enter the advanced search page; select professional search to enable the function. Details are shown in “1.2.5 Professional Search”.

(4) Author search
Click Advanced Search to enter the advanced search page; select author search to enable the function. Details are shown in “1.2.3 author search”.

(5) Sentence Search
Click Advanced Search to enter the advanced search page; select Sentence Search to enable the function. Details are shown in “1.2.4 Sentence Search”.

Journal database recommendation

(1) Introduction to journal database
The journal database shows the composition and resource amount of journals.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, publication content, collection subject, collection period, service mode, publication time, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, Chinese Number, International Standard Serial Number and address.
(3) Online First journals/literature
Online First journals are those published on CNKI in electronic version before print publication. Users can download and print the Literature at the corresponding page. CNKI will offer relevant collection certificate (including the author’s name, Literature tile and publication time) to the author so that the author can provide it to relevant scientific research department of his/her employer. Click the picture of the journal to enter the journal navigation page, and it will show details of the journal selected.
An Online First Literature is a single thesis published in digital version on CNKI via internet (including mobile network) before print publication. Online First literature can be divided into 3 categories as per the editing status during their first issuance: Accepted final draft, typeset final draft and entire issue final draft.
a) An accepted final draft refers to the contribution whose content has been established and passed peer review and the final review for publishing by relevant editor-in-chief.
b) A typeset final draft refers to a contribution which has become an accepted final draft and has been typeset as per required format (including online version format) of a journal. It has established content and format but may not have the publication year, volume, issue and page number.
c) An entire issue final draft refers to a contribution to be printed or digitally published, with established publication year, volume, issue and page number.
Journal article knowledge network node
Basic information
It includes title, author, institution, abstract, fund support, keywords, DOI, class number, page number, pages, size, citing frequency, download, publication information, contents, in-text pictures, authors of citing literature, publication time of Online First literature, version conversion, special identifiers, publication status change, collection, subject, additional materials, copyright statement, etc.
(2) Operation of node literature
Available functions include CAJ download, PDF download, mobile reading, citation, collection, creating citation tracking, printing, sharing, etc., as shown in 1.5.1 Literature Knowledge Network Node.
(3) Knowledge network:
a) Basic information-based knowledge network: Click the author, institution, keywords and fund support to link to corresponding knowledge network node; click in-text pictures to link to the CNKI academic photo gallery; click publication information to link to corresponding publication knowledge network node, i.e. the journal navigation.
b) Literature-based knowledge network: Contains the subject network, citation network and relevant Literature recommendation, as shown in 1.5.1.

Journal video knowledge network node
Journal video knowledge network node entry: journal article knowledge network node > watch the video


Single Database > Theses and Dissertations Database
Theses and Dissertations search
The theses and dissertations database mainly includes four search methods of basic search, advanced search, professional search, and sentence search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
Theses and dissertations database recommendation

(1) Introduction to theses and dissertations database
It displays the composition and resource quantity of theses and dissertations database, and display the excellent degree-awarding institutions on the right bar. Please click to enter the publication navigation page.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, publication content, collection subject, collection period, service mode, publication time, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, Chinese Number, International Standard Serial Number, address, etc.
Dissertations/Theses knowledge network node
Dissertations/Theses knowledge network nodes include the basic information (author, institution), abstract, fund, keywords, mentor, classification codes, article catalog, in-text pictures, Literature publication sources, etc., and provides three download methods of full-text download, chapter-based download and page-based download, as well as two reading methods of mobile reading and online reading. For other functional modules, please refer to 1.5.1 Literature knowledge network node.

See 1.5.2-1.5.7 for other knowledge network nodes.
Single Database > Proceedings Database
Proceedings search
The proceedings database mainly includes five search methods of basic search, advanced search, author search, professional search, and sentence search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
Proceedings database recommendation

(1) Introduction to proceedings database
It displays the composition and resource quantity of proceedings database, and display the excellent proceedings on the right bar. Please click to enter the publication navigation page.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, publication content, collection subject, collection period, service mode, publication time, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, Chinese Number, International Standard Serial Number, address, etc.
Proceedings knowledge network node
Proceedings knowledge network nodes include basic information (author, institution), abstract, fund, keywords, classification codes, conference name, conference time, conference venue, publication source of proceedings, etc. For other functional modules, please refer to 1.5.1 Literature knowledge network node.

Conference video knowledge network node
Conference video entry



See 1.5.2-1.5.7 for other knowledge network nodes.
Single Database > China Core Newspapers Full-text Database
Newspaper search
The newspaper database mainly includes four search methods of basic search, advanced search, professional search, and sentence search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
China Core Newspapers Full-text Database recommendation

(1) Introduction to newspaper database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of newspaper database, and display the excellent newspapers on the right bar. Please click to enter the publication navigation page.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, Literature source, collection subject, collection period, service mode, publication time, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, address, etc.
Newspaper knowledge network node
Newspaper knowledge network nodes include basic information (author, institution), article title, eyebrow head, subhead, body snapshot, newspaper date, edition title, edition number, classification codes, newspaper source, etc. For other functional modules, please refer to 1.5.1 Literature knowledge network node.

See 1.5.2-1.5.7 for other knowledge network nodes.
Single Database > China Yearbooks Full-text Database
Yearbook search
The yearbook database mainly includes three search methods of basic search, advanced search, and professional search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
China Yearbooks Full-text Database recommendation

(1) Introduction to yearbook database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of yearbook database, and display yearbook pictures on the right bar. Please click to enter the publication navigation page.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, Literature source, collection subject, collection period, service mode, publication time, publisher, address, etc.
Yearbook knowledge network node
Yearbook knowledge network nodes mainly include basic information (title, author, institution), statement of responsibility, chief editorial unit, classification codes, column name, language, body snapshot, publication source, etc., with corresponding links for each label. The literature in the same column of yearbook knowledge network node share the same yearbook and column with this item. See 1.5.1 Literature knowledge network node for similar literature and reader recommendation function modules.

See 1.5.2-1.5.7 for other knowledge network nodes.
Single Database > Patents Database
Patents search
The patent database mainly includes three search methods of basic search, advanced search, and professional search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
Patent database recommendation

(1) Introduction to patent database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of patent database.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, Literature source, significant advantages, patent classification, collection period, collection quantity, service mode, update frequency, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, address, etc.
Chinese patent knowledge network node
Chinese patent knowledge network nodes mainly include record information (patent type, application (patent) number, application date, publication number of authorization/application, announcement date of authorization/publicity, applicant, address, inventor, main classification codes, classification codes, country and province codes, number of pages, agency, agent, priority, international application, international publicity, date of entering into the country, original divisional application number), patent legal status, similar patents, the scientific and technological achievements and standards in this field, and research & application. The original-text downloading is also available via CAJ format.
(1) Similar patents: according to collaborative filtering algorithm, patents with similar contents to this patent are recommended.
(2) Scientific and technological achievements and standards in this field: including relevant scientific and technological achievements and relevant standards. The relevant achievements are recommended according to the collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this patent. The relevant standards are recommended according to the collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this patent.
(3) Research and application: including patent development background, patent application condition and research condition of the core technologies involved. The patent development background shows the background of developing this patent. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the word of patent published earlier than this patent in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The patent application condition shows the current application situation of the patent. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the words of patent and application published later than the patent in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The research condition of core technology shows the relative core research condition of this patent. Please click the link for similar literature on the same subject with this patent in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers.

Overseas patent knowledge network node
Overseas patent knowledge network nodes mainly include record information (patent name, application number, application date, publicity number, publicity date, applicant, inventor, main classification codes, classification codes, main and secondary European Classification, priority and abstract), patent legal status, patent items of the same family and foreign similar patents. The full-text downloading method is also available.
(1) Family patents: the patent items sharing the same family with this patent can be shown, that is, click the link to the patent literature that have applied for, been published or approved many times in different countries or regions, as well as in inter-regional patent organizations with the same or basically the same contents.
(2) Similar patents: according to collaborative filtering algorithm, patents with similar contents to this patent are recommended.

Single Database > Standards Database
Standards search
The standard database mainly includes three search methods of basic search, advanced search, and professional search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
Standard database recommendation

(1) Introduction to standard database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of standard database.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, significant advantages, standard classification, collection period, collection quantity, service mode, update frequency, usage instructions, opening instructions, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, address, etc.
National standard knowledge network node
National standard knowledge network nodes mainly include the standard title, standard state, standard number, standard nature, abstract, release date, implementation date, release department, drafters, drafting units, standard technical committee, Chinese standard classification codes, international standard classification codes, the total number of pages, pricing of the hard copy, inter-standard relations, patents and achievements involved in this field, and research & application.
Inter-standard relations: inter-standard relations involve standards cited by this standard, cited standards, substituted standards, superseded standards, and adopted standards.
Patents and achievements involved in this field include patented inventions and scientific and technological achievements designed in this field. The patented inventions are recommended according to the collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this standard. Scientific and technological achievements are recommended according to collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this standard.
Research and application: including the development background of this standard, standard application condition, and research condition of the core technologies involved. The standard development background shows the background of developing this standard. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the word of standard published earlier than this standard in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The standard application condition shows the current application situation of the standard. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the words of standard and application published later than the standard in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The research condition of core technology shows the relative core research condition of this standard. Please click the link for similar literature on the same subject with this standard in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers.

Industry standard knowledge network node
Industry standard knowledge network nodes mainly include standard title, standard state, standard number, abolition date, abstract, release date, implementation or trial implementation date, country, language of the body, release unit, drafting unit, Chinese standard classification codes, international standard classification codes, total number of pages, download pricing, inter-standard relation, patents and achievements involved in this field, and research & application. Among them, the inter-standard relation, patents and achievements involved in this field, and research & application are consistent with those of the national standard knowledge network node.

Domestic and overseas standard bibliographic knowledge network node
Domestic and overseas standard bibliographical reference knowledge network nodes mainly include standard title, standard state, standard number, abolition date, abstract, release date, implementation or trial implementation date, country, language of the body, release unit, drafting unit, Chinese standard classification codes, international standard classification codes, total number of pages, inter-standard relation, patents and achievements involved in this field, and research & application. Among them, the inter-standard relation, patents and achievements involved in this field, and research & application are consistent with those of the national standard knowledge network node.

Single Database > China Science and Technology Achievement Database
Achievements search
Achievements database mainly includes three search methods of basic search, advanced search, and professional search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
Achievements database recommendation

(1) Introduction to achievement database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of achievement database.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, data source, significant advantages, achievement classification, collection period, collection quantity, service mode, update frequency, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, address, etc.
Achievement knowledge network node
Achievement knowledge network nodes mainly include achievement name, the person-in-charge of the achievement, the main unit-in-charge, keywords, achievement introduction, achievement category, the beginning and ending time of the research, evaluation form, filing time of the achievement, similar achievements, patents and standards involved in this field, and research & application.
Similar results: according to the collaborative filtering algorithm, the results similar to the content of this result are recommended
Patents and standards involved in this field: including related patented inventions and related standards. The relevant patented inventions are recommended according to the collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this achievement. The relevant standards are recommended according to the collaborative filtering algorithm with the same subject and similar content as this achievement.
Research and application: including the development background of the achievement, the application condition of the achievement and the research condition of the core technologies involved. The development background of the achievement shows the background of developing this achievement. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the word of achievement published earlier than this achievement in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The application condition of achievement shows the current application situation of the achievement. Please click the link for the similar literature containing the words of achievement and application published later than this achievement in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers. The research condition of core technologies shows the relative core research condition of this achievement. Please click the link for similar literature on the same subject with this achievement in the database of journals, dissertations, proceedings and newspapers.

Single Database > China Ancient Books Database
Ancient books search
The ancient books database mainly includes three search methods of basic search, advanced search, and professional search. For detailed functions, please refer to the corresponding search modes in “1.2 Search Method”.
China Ancient Books Database recommendation

(1) Introduction to the China Ancient Books Database
It displays the collection and resource quantity of the China Ancient Books Database.
(2)Impressum
It displays the publication information of the database, including: introduction, resource characteristics, literature classification, collection period, collection quantity, service mode, update frequency, development unit, competent authority, sponsor, publisher, address, etc.
Ancient books knowledge network node

Personalized Recommendation System > My Follow
“My Follow” shows the user’s personalized content and presents different content to the user in different states. It displays the search type of user subscription and the latest relevant literature, favorite publications, search history, browsing history and download history under the user login status. It displays the user’s search history, view history, and download history while not logged in.

Favorite: Please click the button![]() to favorite the literature to the personal library for the convenience of the user to browse the literature again. It displays the button
to favorite the literature to the personal library for the convenience of the user to browse the literature again. It displays the button![]() through which favorite literature are available in the personal library - My Favorites in the favorite state.
through which favorite literature are available in the personal library - My Favorites in the favorite state.
Citation: Please click the button![]() to pop up the citation window offering citations in three formats: national format, CNKI E-Study and EndNote. In national standard format, the reference content is selected. For the other two, users can click the reference content to select all and directly copy and paste.
to pop up the citation window offering citations in three formats: national format, CNKI E-Study and EndNote. In national standard format, the reference content is selected. For the other two, users can click the reference content to select all and directly copy and paste.

Online reading: Please click the button![]() to enter the online reading interface, as shown below
to enter the online reading interface, as shown below
Download: Please click the button![]() to download literature.
to download literature.
Personalized Recommendation System > Recommendations
It recommends the latest literature, publications and search words based on the user’s personal behavior.

Literature Recommendation
It recommends relevant literature according to the browsing and download history of users. Please refer to “2.3.1 My Follow” for operation on literature.
Publication Recommendation
It recommends publications according to the user’s search behavior. Please click the picture or name of the publication to skip to the publication navigation page
Search Word Recommendation
It recommends the search word according to the user’s search behavior. Please click “search term” to skip to basic search results page and display the search results of the search word in the general database
Personalized Recommendation System > Popular Literature
It displays popular literature, popular journals and hot search words on the whole network or those of a particular subject to show user the literature, journals and search words that all CNKI users follow.
Popular literature
It displays the popular literature on the whole network or that of a particular subject to the user, that is, the literature with the most user operations on the whole network. It displays the popular literature on the whole network if the user does not choose a subject, and display the popular literature of a particular subject if the user chooses a subject under a certain collection. Please refer to “2.3.1 My Follow” for operation on literature..3.1我的关注”。
Popular journals
It displays all popular journals or those of a particular subject to the user. Please click the picture or name of the publication to skip to the publication navigation page.
Buzz word
It displays all buzz words or those of a particular subject to the user. Please click the “search word” to skip to basic search results page and display the search results of the search word in each single database.
Personalized Recommendation System > Personal Library

Please click the function link to enter the corresponding page of the personal library. Please refer to “1.7 personal library” for the functions of the personal library.
The publication source navigation provides the search, browsing and other functions of the publications of the literature source. It takes the whole journal or the contributor unit as the main object to help users understand the publication details of literature source, or find authoritative and high-quality publications and browse literature according to publications.
Navigation entry
Please click “publication search” on the homepage of CNKI to enter the publication source navigation page.

Navigation introduction
Please click![]() to enter the navigation introduction, including navigation collection, coverage range, etc.
to enter the navigation introduction, including navigation collection, coverage range, etc.

Left navigation
The left bar shows the discipline navigation system, including ten major collections and 168 subjects. The user can choose a navigation category to browse all the publication sources under the category. Each single database provides navigation with its own characteristics according to the different knowledge system and structure.

Recent views and recommendations
The homepage of publication source navigation displays the covers or icons of most recently viewed publication sources, and recommends the most recently updated journals, dissertations, proceedings, newspapers and yearbooks and the first two recent updates of reference books. Please click the cover or icon to enter the detail page of publication source.

Publication source search
Switch the search item and enter the search term to search. Then click the literature search to enter the literature search page and switch between navigation search and literature search. As shown in Fig. 3.5..5。

Publication source search results
It displays the search results based on the search criteria. For example, select “source name” to enter the search term “economy” and click “publication source search”:

The Search Result Area shows all the results with publication source name containing “economy”, displaying the quantity of searched items at the top, and the basic information, cover icon, total citations and total downloads of the publication source in the main part. Please click the name or cover image of publication source to enter the detail page of the publication source.
Product navigation
The publication source navigation mainly includes the navigation of journal, monographic serials, degree-awarding unit, conference, newspaper, yearbook and reference book. The user can select the product navigation in the drop-down menu and switch to the navigation homepage of the product, as shown in Fig. 3.7.

As the layout and functions of each single database navigation are roughly the same as those of the publication source navigation, these following descriptions only show the unique features of single database navigation.
Product navigation > General journal navigation
Journals can be searched by journal title (former title), sponsor, ISSN and CN.
Besides of the subject navigation, the left navigation bar also comprises database navigation of journal source, sponsor navigation, publication periodicity navigation, publication place navigation, distribution system navigation and core journal navigation. You can search and browse journals in related fields through the left navigation bar. Click the navigation content, it will return to the page of the journal list in the field.
There are horizontal product category labels: All Journals, Academic Journals, Online First Journals, Exclusive Publishing Journals, Century Journals Project and Single Journals, as shown in the Fig. 3.7.1-1.

The left navigation bar can be combined with the horizontal category labels. For example, click the navigation of “Core journal navigation — > Part II Economy”, then you will see the list of search results; click the label of “journal” and you can get a list of journals as shown in Fig. 3.7.1-2.

Journal navigation search results are as shown in Fig. 3.7.1-3. Check the “Core Journals”, then you can screen the core journals of Peking University from the search results; providing four sorting methods (default, comprehensive influence factor, combined influence factor, cites and the latest update); providing two browsing methods, namely detail and list, for which you can click to switch. Click the cover or name of the journal and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Monographic serials navigation
Monographic serials can be searched by title of the monographic series.
The left navigation bar includes subject navigation, core journal navigation and sponsor navigation.
Providing three sorting methods (default, cites and title); providing two browsing methods, namely detail and list. Click the cover or name of the serials and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Degree-awarding institution navigation
The degree-awarding institutions can be searched by degree-awarding unit name and region.
The left navigation bar includes region navigation and discipline navigation. There are horizontal product category labels: all, doctor and master. The left navigation bar can be combined with the horizontal category labels.
You can screen the degree-awarding institutions according to their categories (all institutions, 211 Project, 985 Project and institutions directly under the Ministry of Education); providing five sorting methods (default, literature number, regions, cites, and downloads); providing two browsing methods, namely detail and list. Click the icon or name of the institutions and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Proceedings navigation
You can search by the names of proceeding title, conference name, sponsor and online publishing contributors in a particular time range.

Proceedings navigation provides searches in proceedings, conferences and sponsor. Labels can be switched as needed to browse and search proceedings, conferences and sponsor.

The left navigation bar includes subject navigation, industry navigation as well as Party and government navigation. The left navigation bar for sponsor includes industry association, institution types and Party and government organizations. The horizontal product category labels of proceedings include: all, domestic, international and video collection. The horizontal product category labels of conferences and organizers include: all, domestic and international. The left navigation bar can be combined with the horizontal category labels.
You can screen the proceedings by the years and types (all, conference proceedings and monograph compilation); provides five sorting methods (default sort, conference date, literature number, cites and downloads). Click the name of the proceedings and you can enter the detail page.

You can screen the conferences by the years and levels (all, international, national, and local); the sorting methods are the same as those of proceedings. Click the conference name and you can enter the related detail page of proceedings.

You can screen the organizers by their nature (all, national association, local association and others). Click the name of the organizers and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Newspaper navigation
You can search the newspapers by using the newspaper title, region, sponsor and CN Number.
The left navigation bar includes newspaper level navigation and publication periodicity navigation.
Provides two sorting methods, default sort and alphabetical order; provides two browsing modes, detailed and list. Click the cover or name of the newspaper and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Yearbook navigation
You can search the yearbooks by using the Chinese title of yearbook, English title of yearbook, keyword, area, editor-in-chief, publisher, ISSN, CN and ISBN.
The left navigation bar includes region navigation, industry navigation, publisher navigation, subject navigation, and yearbook level navigation.
Provides two sorting methods, default sort and alphabetical order; provides two browsing modes, detailed and list. Click the cover or name of the yearbook and you can enter the detail page.

Product navigation > Reference book navigation
You can search the reference books by using the book title, publisher, author and region.
Provides two sorting methods, default sort and alphabetical order; provides two browsing modes, detailed and list. Click the cover or name of the reference book and you can enter the detail page.

Product detail pages > Detail pages of journals/monographic serials
Access to the detail page of journals: search results of journal navigation; knowledge network node of periodical literature > publication sources; search results of literature > publication sources.
The detail page mainly includes a header search bar, introduction, issue browsing, column browsing, statistics and evaluation as well as search results.
Introduction
It incorporates the online publication statement of a single literature in priority journals, functions of the whole issue (collection, RSS subscription, contributing, and sharing), Chinese and English names of journals, databases of journal collection, basic information, publication information and evaluation information. The evaluation information includes influence factors, data collection and journal honors. In this part, three lines is the default, and you can click “More” for all the information.

Issue browsing
The left navigation bar will display the issues and years of journals, including information related to public in priority and online first. Click a year and it will display all the issues of this year. Click an issue, then you can see the catalog on the right, with such information as the column, title, author, page number, etc. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons; click the “Original Catalog Page Browsing”, you can view the cover, catalog and other information of the journal. Printing function is also provided.


Column browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.1.3, column information of the last 10 years is the default on the left, and you can switch labels to view the information of the last 5 years, 3 years or 1 year. The list of literature under a specific column is on the right. The default way of sort is correlation, and other ways include the time, cited count and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons.

Statistics and evaluation
It mainly includes the annual publication overview of journals and latest research hotspots.
The annual publication overview of journals embraces the number of annual articles, the number of annual funding articles and the column distribution of journals in recent decade; the latest research hotspots incorporates the discipline distribution of journals in recent decade and keywords distribution of journals in recent decade. The statistics of the last 20 years is the default on the page and you can also view the statistics of the last 10 or 30 years.
In the diagram of the “Keywords distribution of journals in recent decade”, you can view the volume of literature on electronic structure in the last 20 years by clicking the bar of “electronic structure”, among which the bar chart will display the annual literature count about “electronic structure” while the line chart will show the ratio of “electronic structure” related literature count to the total literature count of that year. You can then click the keyword “molecular dynamics” to view the literature count in the last 20 years and compare the situation of the two keywords as shown in the following figures.


Search results
Set a search condition such as a topic, title, author and keyword. Enter related words and click the “Search” button, you can view the search results.
The groups of the search results, including the year, discipline and fund, will be displayed on the left. Click the “Unfold” button and you can view all the group contents.
The search results are on the right, displaying the literature’s title, author, year/issue, cited count and download count. The default way of sort is correlation, and other ways include time, cited count and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons

Product detail pages > Detail page of degree-awarding institution
Access to the detail page of degree-awarding institution: search results of degree-awarding institution navigation; knowledge network node of dissertation literature > publication sources; search results of literature > publication sources.
The detail page mainly includes a header search bar, discipline and specialty browsing, discipline statistical statement, and search results.
Introduction
As shown in Fig. 3.8.2.1, Icon 1 displays the labels of degree-awarding institutions such as Project 211, Project 985, and institutions directly under the Ministry of Education. Icon 2 displays product category labels, including all categories, doctors and masters. After clicking the label of “doctors”, for example, it will display the information of doctoral dissertations of the institution. Icon 3 comprises basic information and publication overview. Among them, the “publication overview” shows the literature count, cited count and download count. Icon 4 provides the collection and sharing functions for the degree-awarding institution.

Discipline and specialty browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.2.2, the major navigation of the degree-awarding institution will be displayed on the left. Move the cursor on a discipline field, you can view its first and second-level disciplines and specialties. Click the navigation content, the literature list of the discipline and specialty will be unfolded on the right, including the title, author, supervisor, degree-awarding year, dissertation level, cited count and download count. The default way of sort is correlation, and other ways include the degree-awarding year, level of excellent dissertation, cited count and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons.

Discipline statistical statement
There are labels of statistical reports and statistical charts on the left, and the former is the default. The statistical statements of disciplines and specialties of the degree-awarding institution will be displayed on the right, showing a certain category’s first-level disciplines, disciplines and specialties, supervisors count of both doctors and masters, literature count, total cited count, total download count and total funded literature count. Click a category of disciplines, you can unfold the statistics of its first-level disciplines; click a first-level discipline and you can view the statistics of its specialties, as shown in Fig. 3.8.2.3-1.

As shown in Fig. 3.8.2.3-2, click the left statistical chart, and the right side will display the annual distribution of literatures, distribution of funding sponsored articles (Annual distribution of funding sponsored articles, The distribution of the TOP15 funding projects and The distribution of the TOP15 first level disciplines in funding articles), and supervisor distribution. Click the column of a supervisor in the chart of the literatures directed by the supervisor, you can see the annual trend chart of supervised literature by the supervisor and the distribution diagram of disciplines that each literature belongs to.

Search results
Set a search condition such as topic, title, author and supervisor. Enter related words and click the “Search” button, you can view the search results as shown in Fig. 3.8.2.4. The groups of the search results, including the year of degree, discipline and specialty, supervisor and fund, will be displayed on the left. Click the “Unfold” button, and you can see all contents in that group. The list of search results is on the right.

Product detail pages > Detail page of proceedings
Access to the detail page of proceedings: search results of proceedings navigation; knowledge network node of conference proceedings > publication sources; search results of literature > publication sources.
The detail page mainly includes a header search bar, proceedings of this conference, serial proceedings, and search results of the proceedings.
Introduction
As shown in Fig. 3.8.3.1, the cover image of the proceedings is on the left while the basic information and publication overview are on the right. The publication overview displays the literature count, total cited count, total download count, series name and subject name. You can find the collection and sharing functions for the proceedings at the upper right.

Proceedings of this conference
As shown in Fig. 3.8.3.2, the list of all the proceedings at this conference will be displayed on the left while the literature list of the selected proceedings, including title, author, page number, cited count and download count, will be shown on the right. The list is sorted in ascending order of the page number by default, and you can also set the sort condition in other ways such as title, cited count and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons.

Serial proceedings
As shown in Fig. 3.8.3.3, this part displays the relevant proceedings information in the conference series to which this paper belongs, including the conference time, title of the proceedings, literature count, funded literature count, cited count and download count. This is shown in the reverse order of the conference time.

Search results
Set a search condition such as topic, title, author and keyword. Enter related words and click the “Search” button, you will see the search results as shown in Fig. 3.8.3.4. The groups of the search results, including the discipline and fund, will be displayed on the left. Click the “Unfold” button, you can view all the contents in the group. The list of search results is on the right.

Product detail pages > Detail page of conference organizers
It mainly includes a header search bar, serial conferences, serial proceedings, and relevant/local chapters. The header search bar is the same as that in the navigation home page.
Serial conferences
As shown in Fig. 3.8.4.1, by switching the labels, You can view all the conferences and proceedings of the host organization as well as national or international conferences and proceedings. The left side displays the name of the serial conferences organized by the organizers, while the right side shows the conference information of the selected serial conferences in the abstract mode, including the conference name, time, venue, level, literature count, download count, and cited count. The information is sorted in the reverse order of the conference time by default, you can also set the sort condition in other ways such as the literature count, download count and cited count.

Serial proceedings
The left side displays the name of the serial conferences/proceedings organized by the organizers, while the right side shows the proceedings information of the selected serial conferences/proceedings in the abstract mode, including the proceedings name, time, literature count, download count, and cited count. The information is sorted in the reverse order of the conference time by default, you can also set the sort conditions in other ways such as the number of literatures, download count and number of citations, as shown in Fig. 3.8.4.2.

Relevant/local chapters
This part displays relevant and local chapters of the organizers, including relevant first-level chapters, relevant chapters, specialized committee, and relevant local chapters. The presentation of the relationships among the organizers in layers as shown in Fig. 3.8.4.3.

Product detail pages > Detail page of newspapers
Access to the detail page of newspapers: search results of newspaper navigation; knowledge network node of newspapers > publication sources; search results of literature > publication sources.
The detail page mainly includes a header search bar, introduction, date browsing, column browsing, and search results.
Introduction
As shown in Fig. 3.8.5.1, the introduction includes the basic information, contact information and publication overview. Among them, the “publication overview” includes the number of literatures, download count, and cited count. In this part, three lines is shown by default and you can click “More” for all the information. You can find the collection and sharing functions for the newspapers at the upper right.

Date browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.5.2, the left side displays the date of publication. Choose the year first, and it will show the months of publication. Move the cursor to a month, and you can see the publication date. Click the date, the right side will display the newspapers published on that day, with the title, author, edition number, column, and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons.

Column browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.5.3, column information of the last 10 years is shown by default on the left and you can switch the labels to view the information of the last 5 years, 3 years or 1 year. The list of literature under a specific column is on the right.

Search results
Set a search condition such as topic, title, author and keyword. Enter related words and click the “Search” button, you can view the search results as shown in Fig. 3.8.5.4. The groups of the search results, including the year, discipline and affiliation, will be displayed on the left. Click the “Unfold” button and you can view all the group contents. The list of newspaper search results is on the right.

Product detail pages > Detail page of yearbook
Access to the detail page of yearbook: search results of yearbook navigation; knowledge network node of yearbook > publication sources; search results of literature > publication sources.
The detail page mainly includes a header search bar, introduction, year browsing, column browsing, evaluation and recommendation, and search results. The header search bar is the same as that in the navigation home page.
Introduction
As shown in Fig. 3.8.6.1, the introduction displays the basic information of the yearbook in the latest year.

Year browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.6.2, the left side displays the year and volume information of the yearbook while the right side shows the catalog under the selected year and volume. You can click![]() to unfold directories at lower levels and click
to unfold directories at lower levels and click ![]() to fold them. The items are sorted in the order of page numbers. You can click the name of an item to enter its knowledge network node.
to fold them. The items are sorted in the order of page numbers. You can click the name of an item to enter its knowledge network node.

Column browsing
As shown in Fig. 3.8.6.3, the first-level column information of the yearbook is shown by default on the left. The right side shows the entry list of the column, including the title, column name, year (volume), page number, and download count. You can also screen the item types such as the literature, statistical charts, facts, organizations as well as laws and regulations. It is sorted in a correlation order by default and you can also set the sort conditions in other ways such as year and download count. Click a title then you can enter the knowledge network node of the corresponding item; Move the cursor to a literature, you can download (logged status), preview and share the literature by clicking corresponding buttons.

Evaluation and recommendation
As shown in Fig. 3.8.6.4, evaluation and recommendation part displays the citation of the yearbook and other yearbooks of the same kind. You can click the cited number of the citing literature list to view the citing literature which cite the yearbooks of that year.

Search results
Set a search condition such as title, text, chief editor and affiliations. Enter related words and click the “Search” button, you can view the search results as shown in Fig. 3.8.6.5. The groups of the search results, including the item types, year and disciplines, are displayed on the left. Click the “Unfold” button, you can view all the group contents. The list of search results is on the right.




